
Table of Contents
Introduction
Cholesterol is often viewed negatively, but it’s a vital component of our body, essential for producing hormones, vitamin D, and substances that help digest foods. However, you can lower your cholesterol and still maintain the benefits of good health. An imbalance—specifically high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol—can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease. This article explores various foods that can help lower your cholesterol, elucidating their benefits and how they can be seamlessly integrated into daily diets.
Understanding Cholesterol
What is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in all cells of the body. It’s crucial for the formation of cell membranes, vitamin D synthesis, and the production of hormones. While the body produces enough cholesterol for these functions, it’s also obtained from dietary sources. However, not all cholesterol is created equal, and managing its levels is essential for overall health.
Cholesterol travels through the bloodstream in particles known as lipoproteins. These lipoproteins are categorized mainly into two types: LDL and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). The balance between these types is a significant determinant of health, particularly cardiovascular health.
Types of Cholesterol: HDL vs. LDL
LDL cholesterol is often referred to as bad cholesterol because it can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. On the other hand, HDL cholesterol is recognized as good cholesterol; it helps remove other forms of cholesterol from the bloodstream. A higher level of HDL is generally associated with a lower risk of heart disease.
Understanding the balance between these two types is crucial for individuals looking to manage their cholesterol levels effectively. Regular health check-ups that measure these cholesterol types can provide important insights and guide dietary choices.
By understanding how to lower your LDL Cholesterol and increase HDL Cholesterol through dietary choices, you can take proactive steps toward better health.
Foods vs. Supplements
Natural Foods for Cholesterol Management
Incorporating specific foods into your diet can significantly impact cholesterol levels. Foods rich in soluble fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and plant sterols are particularly beneficial. Examples include oats, barley, beans, lentils, avocados, and various fruits and vegetables. A balanced diet that emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods can help improve cholesterol profiles.
Natural foods often come with additional nutrients and health benefits, making them preferable to supplements. They promote overall heart health and can contribute to other health aspects, such as weight management and improved digestion.
Effectiveness of Supplements to Lower Cholesterol
While dietary supplements can be useful for managing cholesterol, they should not replace a healthy diet. Common supplements like fish oil, plant sterols, and soluble fiber can assist in lowering LDL cholesterol levels. However, individuals should consult healthcare providers before starting any supplement regimen, ensuring safety and efficacy.
Other supplements that have been shown to be helpful include:
Red Yeast Rice
Magnesium orotate
Potassium orotate
K-MG (Pot-mag aspartate)
Chromium GTF
L-Carnitine
Lecithin granules
Coenzyme B Complex
Krill oil
Seanol
It is also important to note that supplements may not provide the same breadth of benefits as whole foods. The synergistic effects of nutrients found in natural foods can enhance their overall health benefits, making them a more holistic choice for cholesterol management.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Sources of Omega-3
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that have numerous health benefits, including lowering triglycerides and promoting heart health. Primary sources include fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help improve your cholesterol levels effectively.
For those who may not consume enough fish, omega-3 supplements derived from fish oil or algae are viable alternatives. These supplements can help bridge the gap in omega-3 intake, especially for vegetarians and vegans.
Benefits for Cholesterol Levels
Research indicates that omega-3 fatty acids can help lower triglyceride levels, which, when elevated, can contribute to a higher risk of heart disease. Additionally, these fats may improve endothelial function and reduce inflammation, both of which are crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health.
Incorporating omega-3-rich foods into a balanced diet can lead to improved cholesterol metrics, enhancing overall health and well-being.
Increasing HDL (Good Cholesterol)
Foods to Boost HDL
To enhance HDL cholesterol levels, certain foods can play a pivotal role. Foods rich in healthy fats, such as olive oil, avocados, and nuts, can help raise HDL levels. Additionally, fatty fish and high-fiber foods are also beneficial.
Regular consumption of foods like dark chocolate and red wine, in moderation, has been shown to support HDL levels due to their antioxidant properties. Including these foods can contribute to a healthier lipid profile, promoting better heart health.
Lifestyle Changes to Enhance HDL
In addition to dietary modifications, lifestyle changes play a significant role in increasing HDL levels. Regular physical activity, particularly aerobic exercises, can effectively boost HDL cholesterol. Engaging in activities such as running, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week is recommended.
Quitting smoking and maintaining a healthy weight are also crucial in raising HDL levels. These lifestyle adjustments, combined with a heart-healthy diet, create a robust strategy for improving cholesterol profiles.
Lowering LDL (Bad Cholesterol)
Foods That Help Lower LDL
To effectively lower LDL cholesterol, incorporating specific foods into your diet is essential. Foods high in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, lentils, and certain fruits like apples and citrus, can help lower LDL levels. These foods work by binding cholesterol in the digestive system, preventing its absorption into the bloodstream.
Additionally, incorporating nuts, especially almonds and walnuts, and using healthy fats like olive oil can further contribute to lowering LDL cholesterol. These foods not only aid in cholesterol management but also provide essential nutrients and promote overall health.
Impact of Fiber on LDL Levels
Dietary fiber plays a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels. Soluble fiber, in particular, has been shown to reduce LDL cholesterol effectively. It absorbs water and forms a gel-like substance in the gut, which can bind to cholesterol and bile acids, aiding in their excretion from the body.
Research suggests that a daily intake of at least 5 to 10 grams of soluble fiber can lead to significant reductions in LDL levels. Incorporating fiber-rich foods into meals ensures a balanced approach to cholesterol management.
Lowering Triglycerides
Key Foods to Reduce Triglycerides
Triglycerides, another type of fat found in the blood, can also contribute to heart disease when elevated. Consuming foods low in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats is crucial for managing triglyceride levels. Emphasizing whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate these levels.
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish and flaxseeds, are particularly effective in lowering triglycerides. Regularly including these foods can promote better heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Role of Exercise in Triglyceride Management
Exercise plays a vital role in managing triglyceride levels. Engaging in regular aerobic activity not only helps burn calories but also improves overall lipid profiles, including triglycerides. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week.
Combining aerobic exercises with strength training can further enhance triglyceride management, promoting overall health and well-being. This multifaceted approach ensures that cholesterol and triglyceride levels remain within a healthy range.
Risk of High Cholesterol
Health Implications
High cholesterol levels can lead to severe health complications, primarily cardiovascular diseases. Elevated LDL cholesterol contributes to plaque formation in the arteries, narrowing them and increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. It’s essential to recognize these risks and take proactive steps to manage cholesterol levels.
Beyond cardiovascular issues, high cholesterol can lead to other health complications, including peripheral artery disease, which affects blood flow to the limbs, and pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas. Understanding these risks highlights the importance of maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
Statistics on High Cholesterol
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly 95 million American adults have total cholesterol levels higher than 200 mg/dL, a level considered borderline high. This statistic underscores the urgent need for awareness and action regarding cholesterol management.
The rising prevalence of high cholesterol correlates with lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity, all of which can be addressed through lifestyle changes and dietary interventions.
Heart Disease and Cholesterol
Connection Between High Cholesterol and Heart Disease
The relationship between cholesterol levels and heart disease is well established. High levels of LDL cholesterol contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by plaque buildup in the arteries. This can significantly impair blood flow, leading to serious cardiovascular events.
Conversely, higher levels of HDL cholesterol are associated with a lower risk of heart disease, as HDL helps transport cholesterol away from the arteries and back to the liver for excretion. Understanding this balance is crucial for individuals looking to protect their heart health.
Preventative Measures
Preventing heart disease involves a multifaceted approach that includes regular health screenings, a heart-healthy diet, and an active lifestyle. Monitoring cholesterol levels through routine check-ups enables early intervention and management.
Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, alongside engaging in regular physical activity, can significantly reduce the risk of developing heart disease. These lifestyle changes not only improve cholesterol levels but also enhance overall well-being.
Energy and Cholesterol
How Cholesterol Affects Energy Levels
Cholesterol plays a critical role in cellular energy metabolism. It is involved in forming cell membranes, which are essential for nutrient absorption and energy production. However, imbalanced cholesterol levels can lead to fatigue and reduced energy levels, as cells may not function optimally.
Managing cholesterol levels through diet and lifestyle choices not only supports heart health but also enhances energy levels, allowing for better physical and mental performance.
Balancing Energy Intake and Cholesterol
Balancing energy intake with cholesterol management requires a focus on nutrient-dense foods. Consuming whole foods that provide essential nutrients while being mindful of cholesterol levels can lead to improved health outcomes.
Incorporating foods high in fiber and healthy fats, while limiting refined sugars and saturated fats, supports energy balance and effective cholesterol management, ensuring optimal health and vitality.
The 4:1 Ratio of Oils
Understanding Oil Ratios
The 4:1 ratio of oils refers to the balance between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids in cooking oils. A healthy ratio can support heart health and reduce the risk of inflammation. Many traditional cooking oils, such as corn and soybean oil, are high in omega-6 fatty acids, which can promote inflammation when consumed excessively.
Conversely, incorporating oils rich in omega-3s, such as flaxseed oil or fish oil, can help maintain this balance, promoting better lipid profiles and overall health.
Best Oils for Cholesterol Management
When selecting oils for cooking, choose those with favorable fatty acid profiles. Olive oil and avocado oil are excellent choices for cholesterol management due to their heart-healthy fat content. These oils can help lower LDL levels while supporting overall cardiovascular health.
Utilizing a variety of healthy oils can enhance the flavor of meals while promoting better cholesterol management and overall wellness.
Carbohydrates and Cholesterol
How Carbohydrates Convert to Cholesterol
Carbohydrate consumption has a direct impact on cholesterol levels. When refined carbohydrates and sugars are consumed in excess, they can lead to insulin resistance and increased fatty acid synthesis in the liver, contributing to higher triglyceride and LDL cholesterol levels.
Understanding the types of carbohydrates consumed is crucial. Opting for complex carbohydrates found in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables can support better cholesterol management compared to simple sugars and refined grains.
Managing Carbohydrate Intake
To manage cholesterol levels effectively, it’s essential to focus on the quality of carbohydrates consumed. Integrating whole grains, fruits, and vegetables into meals while limiting refined sugars can lead to improved cholesterol profiles.
Keeping track of carbohydrate intake and choosing nutrient-dense options can significantly influence overall health and cholesterol management, creating a balanced and heart-healthy diet.
Conclusion
Managing cholesterol levels is a critical aspect of maintaining overall health and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. By incorporating specific foods, making lifestyle changes, and understanding the types of cholesterol, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their cholesterol profiles. Emphasizing whole foods, regular exercise, and mindful carbohydrate intake creates a robust foundation for heart health.
As the conversation around cholesterol continues to evolve, being informed and making intentional dietary choices remains essential. A balanced approach that prioritizes nutrient-dense foods can pave the way for better health outcomes and enhanced well-being.
FAQs
What foods should I avoid to lower cholesterol?
Avoid foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as fried foods, baked goods, and processed snacks. Limiting red meat and full-fat dairy products is also advisable.
How often should I get my cholesterol checked?
It’s recommended to have your cholesterol checked every 0ne to two years, but more frequent testing may be necessary if you have risk factors for heart disease.
Can I lower my cholesterol without medication?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as improving your diet, increasing physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly lower cholesterol levels without the need for medication.
Is all cholesterol bad?
No, the key is to maintain a healthy balance between LDL and HDL. Some LDL is good and some HDL is bad.
How quickly can diet changes affect cholesterol levels?
Diet changes can begin to affect cholesterol levels within a few weeks. However, for significant changes, it may take several months of consistent healthy eating to see results.
Products
At Home Tests
-
←→

OmegaQuant Complete Test Kit
$114.95Maximum quantity exceededMinimum purchase amount of 0 is required -
←→

-
←→
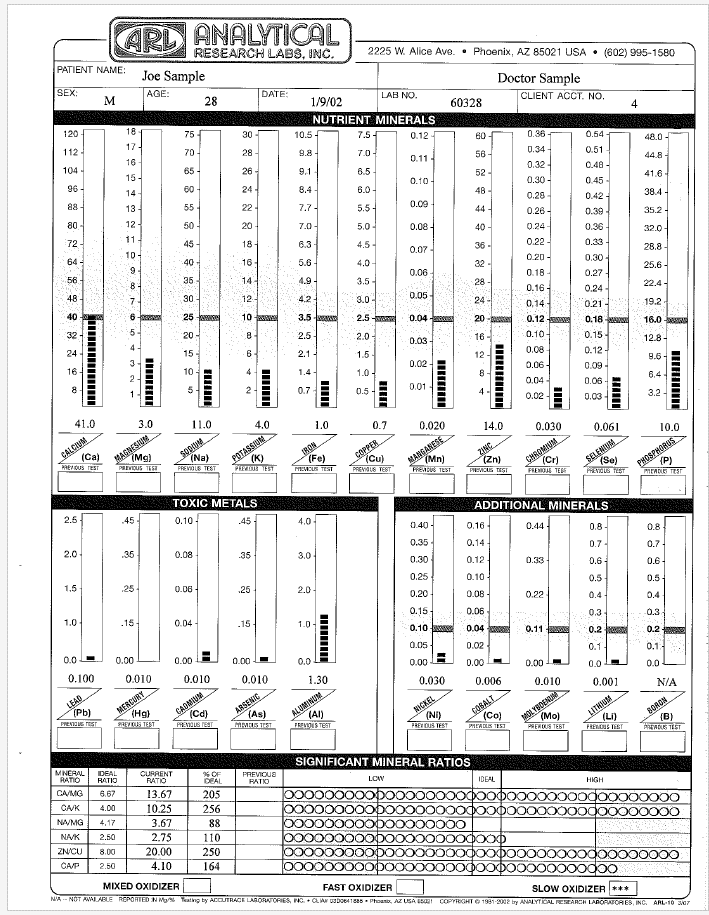
Analytical Research Labs Hair Test
$179.00$149.00Providing a mineral blueprint of one’s biochemistry, an Analytical Research Labs Hair Minerals Test reports levels of minerals and heavy metals in your body giving possible reasons for your symptoms, with suggestions for nutritional supplements and diet changes. Hair tissue mineral analysis can provide pertinent information about balanced nutrition, one’s metabolic rate, energy levels, sugar and carbohydrate tolerance, stage of stress, immune system and glandular activity.- Buy 2 at $145.00
Analytical Research Labs Hair Test
$179.00 $149.00Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
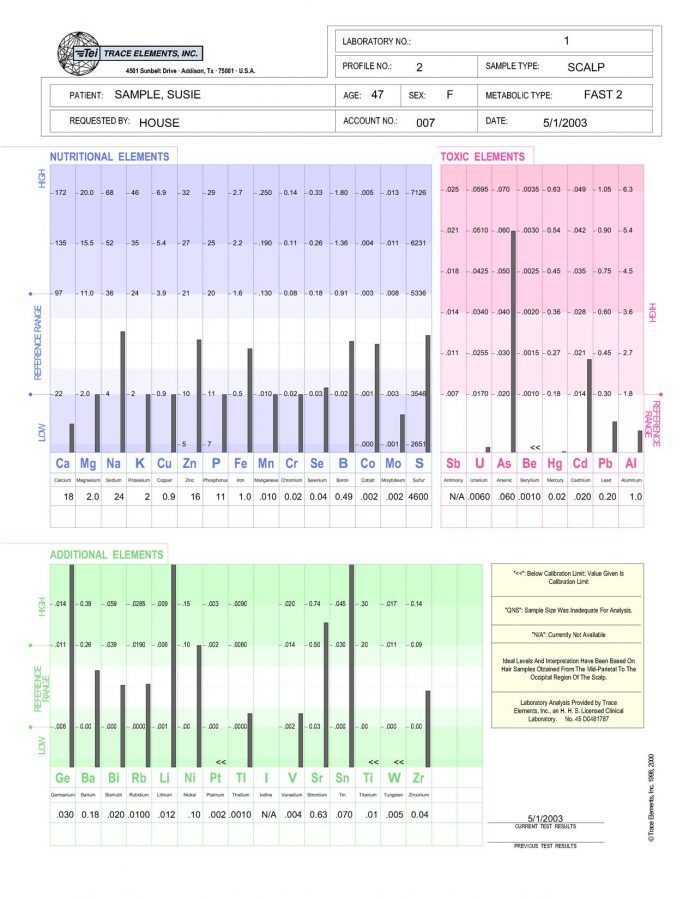
Trace Elements Nutritional Deficiencies Hair Test
Nutritional Tests, At Home Health Tests, Toxic Metals Tests, Hair Tests, Autism Tests, Immune System Tests$188.00 $148.00Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart...
Supplements
-
←→
Magnesium Orotate
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Heart Solutions, Immune System Solutions, Gastrointestinal Solutions, Allergy Solutions$25.10Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→

Potassium Orotate
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Skin Solutions, Diabetes Solutions, Heart Solutions, Muscle Solutions, Hormone Solutions, Gastrointestinal Solutions$23.40Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
K-MG Potassium Magnesium
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Headache Solutions, Heart Solutions, Muscle Solutions, Lung Solutions, Memory Loss Solutions, Anxiety, Stress, Depression Solutions$13.10Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→

GTF Chromium Glucose Tolerance Factor
$4.60GTF Chromium Glucose Tolerance Factor with 200 mcg ChromiumGTF Chromium Glucose Tolerance Factor
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Diabetes Solutions, Skin Solutions, Heart Solutions, Muscle Solutions, Anxiety, Stress, Depression Solutions, Fatigue Solutions$4.60Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
L-Carnitine w/ B1
Supplements, Amino Acids Supplements, Hormone Solutions, Heart Solutions, Muscle Solutions, Lung Solutions$18.60Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart...
References
- https://links.e.response.mayoclinic.org/EmailPreview-GeneralHealth
- https://store.mayoclinic.com/health/vitamins-supplements.html
- https://order.store.mayoclinic.com/flex/mmv/HLDIGAR/?altkey=HLEMORG
- https://order.store.mayoclinic.com/flex/mmv/FHBLC01/?altkey=FHBORG
- https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/red-yeast-rice
