
Table of Contents
Introduction to Rheumatoid and Osteoarthritis
Arthritis is a term that encompasses a range of inflammatory joint diseases, with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA) being among the most prevalent. Understanding the underlying causes, including the contributing role of toxic metals, is crucial for effective management and symptom relief. This article aims to explore the relationship between toxic metals and arthritis, highlighting how these substances can exacerbate symptoms and discussing strategies for detoxification and overall joint health.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints. In this condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. This results in inflammation, pain, and eventual joint damage. Common symptoms include swollen joints, morning stiffness, fatigue, and a general sense of malaise. RA can also affect other systems in the body, leading to complications in the lungs, heart, and eyes.
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis, on the other hand, is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage—the protective tissue at the ends of bones. As cartilage wears away, bones begin to rub against each other, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced mobility. OA is often associated with aging, overuse, and injuries, and common symptoms include joint pain during movement, stiffness after resting, and swelling in the affected areas.
Common Symptoms and Challenges
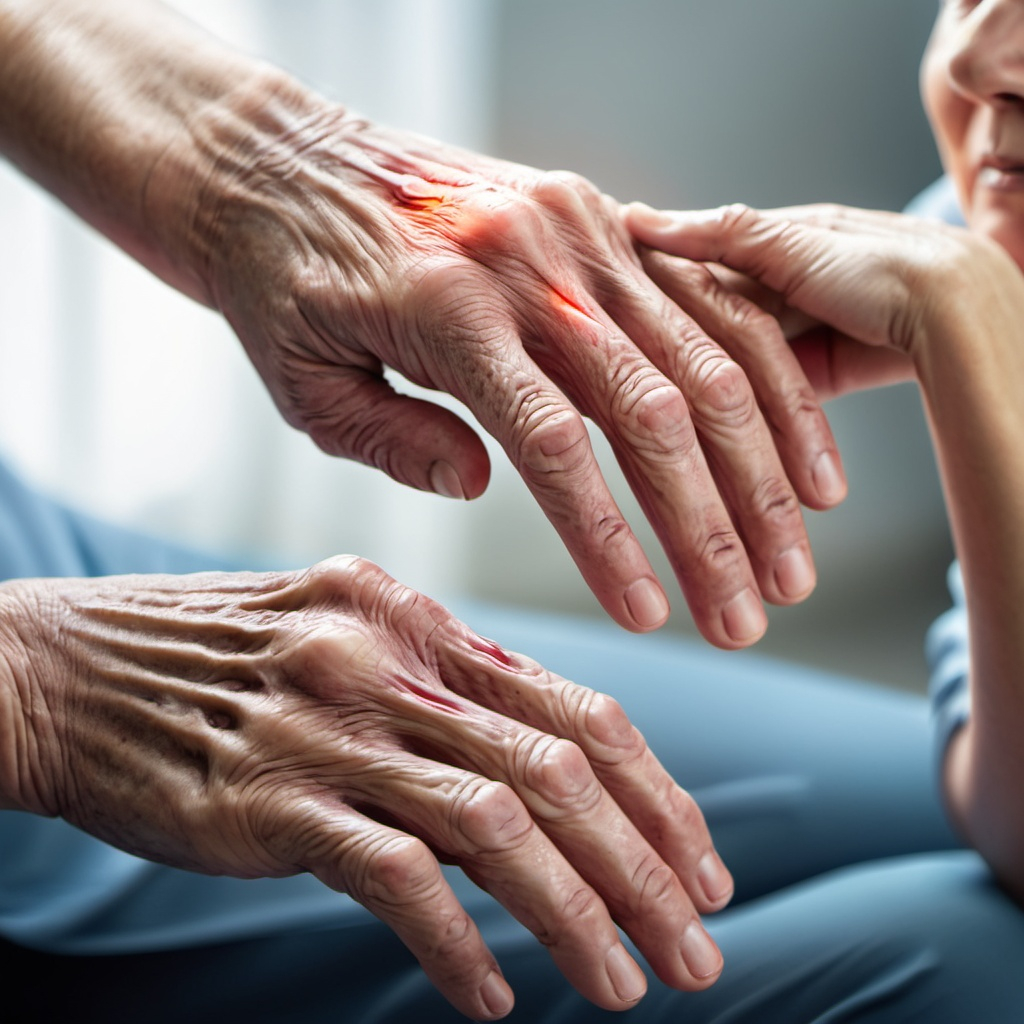
For individuals suffering from either rheumatoid or osteoarthritis, everyday activities can become challenging. Tasks such as walking, climbing stairs, or even gripping objects can become painful and difficult. The emotional toll of living with chronic pain can also lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and depression. Therefore, understanding and addressing the underlying factors contributing to these conditions, such as toxic metal exposure, is essential for improving overall health and well-being.
The Role of Toxic Metals in Arthritis
Overview of Toxic Metals
Toxic metals such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and arsenic can enter the body through various sources, including contaminated food, water, air, and consumer products. These metals can accumulate in bodily tissues and organs, leading to harmful health effects. Research has shown that these toxic substances can trigger inflammatory responses and exacerbate existing health conditions, including arthritis. Their presence in the body can interfere with normal cellular function, leading to increased oxidative stress and inflammation.
How Toxic Metals Accumulate in the Body
The accumulation of toxic metals often occurs through prolonged exposure. For instance, lead can be ingested through old paint or plumbing, while mercury exposure can occur through certain types of fish or dental amalgams. Once inside the body, these metals can remain for years, as they are not easily excreted. The build-up can lead to systemic toxicity, impacting various organs and contributing to the progression of inflammatory diseases like arthritis.
Hair Analysis: A Key to Identifying Toxic Metal Exposure
What is Hair Analysis?
Hair analysis is a non-invasive technique used to assess the levels of various metals and minerals in the body. By analyzing hair samples, healthcare providers can identify patterns of mineral deficiency and toxic metal accumulation. This method is particularly useful for chronic conditions where traditional blood tests may not provide a complete picture of mineral status.
Interpreting Hair Analysis Results
The results from hair analysis can provide valuable insights into a person’s exposure to toxic metals. Elevated levels of specific metals in the hair can indicate ongoing exposure, while deficiencies in essential minerals may highlight areas for dietary improvement. Understanding these results allows for targeted interventions, such as detoxification protocols and dietary adjustments.
Benefits of Hair Analysis for Arthritis Patients
For arthritis patients, hair analysis can serve as a critical tool for personalized treatment approaches. By identifying toxic metal burdens and nutritional deficiencies, individuals can work with healthcare providers to develop tailored detoxification strategies. These strategies can help minimize inflammation, enhance joint function, and refine dietary practices to support overall health.
Impact of Toxic Metals on Rheumatoid and Osteoarthritis
Specific Toxic Metals and Their Effects
Various toxic metals have been studied for their potential impact on arthritis symptoms. For example, lead exposure has been linked to increased severity of joint symptoms, particularly in rheumatoid arthritis. Similarly, cadmium has been associated with an increased risk of developing osteoarthritis. The mechanisms through which these metals exacerbate symptoms include promoting oxidative stress, inflammation, and immune system dysfunction.
How Toxic Metals Exacerbate Symptoms
Toxic metals can interfere with the body’s natural inflammatory processes, leading to increased pain and swelling in joints. They may also contribute to the breakdown of cartilage and bone tissue, further worsening the degenerative changes seen in osteoarthritis. Furthermore, these metals can affect the metabolism of essential nutrients, leading to deficiencies that impede healing and recovery. As a result, managing exposure to these toxic substances is crucial for alleviating arthritis symptoms.
Supplementing for Relief: Addressing Toxic Metal Build-Up
Detoxification Supplements
There are several detoxification supplements that can assist in removing toxic metals from the body. Compounds such as chlorella, spirulina, and cilantro are known for their ability to bind to heavy metals and facilitate their excretion. Additionally, supplements containing antioxidants like vitamin C and E can help mitigate oxidative stress caused by toxic metal exposure. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Vitamins and Minerals to Support Joint Health
In addition to detoxification supplements, certain vitamins and minerals play a vital role in supporting joint health. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce joint stiffness and pain. Vitamin D is crucial for bone health, and magnesium aids in muscle relaxation and reduces muscle cramps. Including a balanced intake of these nutrients can provide additional support for arthritis management.
The Connection Between Obesity and Arthritis
How Obesity Influences Arthritis Symptoms
Obesity is a significant risk factor for the development and progression of arthritis. The excess weight places additional stress on weight-bearing joints, leading to an increased risk of joint damage and pain. Furthermore, adipose tissue releases pro-inflammatory cytokines, which can exacerbate inflammation in the body and worsen arthritis symptoms. Thus, addressing obesity is crucial for individuals with arthritis.
Role of Toxic Metals in Weight Gain
Toxic metals have been implicated in contributing to weight gain and obesity. For instance, studies suggest that certain metals can disrupt endocrine function, leading to metabolic disorders that promote weight accumulation. Additionally, heavy metals may interfere with the body’s ability to process nutrients effectively, leading to imbalances that increase the risk of obesity. Understanding this connection is vital for developing comprehensive strategies for weight management in arthritis patients.
Allergies and Their Relationship with Arthritis
Common Allergens Linked to Arthritis Flare-Ups
Allergies can also play a role in exacerbating arthritis symptoms. Common allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, and certain food products, can trigger inflammatory responses in susceptible individuals. These responses can lead to increased joint pain and stiffness, particularly in those with rheumatoid arthritis. Identifying and managing these allergens is crucial for minimizing flare-ups and enhancing overall quality of life.
Reducing Allergens in Your Environment
To reduce exposure to allergens, individuals can take several steps to improve their home environment. Regular cleaning to eliminate dust and pet dander, using air purifiers, and avoiding known food allergens can significantly decrease inflammatory responses. Creating a less allergenic environment is essential for managing both allergies and arthritis more effectively.
The Importance of Exercise in Managing Arthritis
Types of Exercise Beneficial for Arthritis Patients
Exercise is a key component in managing arthritis symptoms. Low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling, and walking can enhance joint function and reduce stiffness without putting excessive stress on the joints. Strength training exercises can also be beneficial, as they help to build muscle around the joints, providing better support and stability. Regular physical activity can lead to improved mobility and a reduction in pain levels.
How Exercise Can Help Detoxify the Body
In addition to improving joint health, exercise can also support the body’s natural detoxification processes. Physical activity increases circulation, promoting the efficient transport of nutrients and the removal of waste products. Sweating during exercise can help eliminate certain toxins, including metals, through the skin. Incorporating regular exercise into daily routines can therefore be a holistic approach to managing arthritis and reducing toxic metal accumulation.
Understanding Toxic Chemicals and Their Effects
Common Sources of Toxic Chemicals
Toxic chemicals can be found in many everyday products, from household cleaners and personal care items to pesticides and industrial materials. Common sources include bisphenol A (BPA) in plastics, phthalates in fragrances, and heavy metals in certain paints and plumbing materials. Awareness of these sources is vital to minimize exposure and protect joint health, especially for those with pre-existing arthritis.
Strategies to Minimize Exposure
To reduce exposure to toxic chemicals, individuals can adopt several strategies. Opting for natural cleaning products, using glass or stainless steel containers instead of plastic, and choosing personal care products that are free from synthetic fragrances and harmful additives can significantly lower the risk of chemical exposure. Regularly checking labels and being informed about product ingredients are essential practices for safeguarding health.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Health
Empowering Yourself Against Toxic Exposures
Taking control of one’s health involves a proactive approach to understanding the impact of toxic metals and chemicals on arthritis. By identifying sources of exposure, pursuing detoxification strategies, and adopting a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life. Empowerment comes from knowledge, and being informed about the role of environmental factors in arthritis can lead to better management strategies.
Seeking Professional Guidance for Arthritis Management
For those battling arthritis, consulting with healthcare professionals such as rheumatologists, nutritionists, and holistic health practitioners can provide tailored support. These experts can offer personalized advice on managing symptoms, dietary recommendations, and appropriate detoxification protocols. Through a comprehensive and informed approach, individuals can enhance their health, reduce the impact of toxic metals, and improve their overall well-being.
FAQ’s
What are the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
Common symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include joint pain, swelling, morning stiffness, fatigue, and reduced range of motion. It may also lead to systemic complications affecting other organs.
How do toxic metals contribute to arthritis?
Toxic metals can trigger inflammatory responses, interfere with normal cellular functions, and exacerbate oxidative stress, contributing to joint pain and degeneration.
How is hair analysis used for in arthritis management?
Hair analysis helps identify levels of toxic metals and mineral deficiencies, allowing for targeted detoxification strategies and nutritional support.
Can exercise help alleviate arthritis symptoms?
Yes, regular exercise can improve joint function, reduce stiffness, and enhance overall mobility. Low-impact activities are particularly beneficial.
How can I reduce my exposure to toxic chemicals?
Minimize exposure by opting for natural products, using glass containers instead of plastic, and regularly checking labels on personal care and cleaning items.
Products
At Home Tests
-
←→
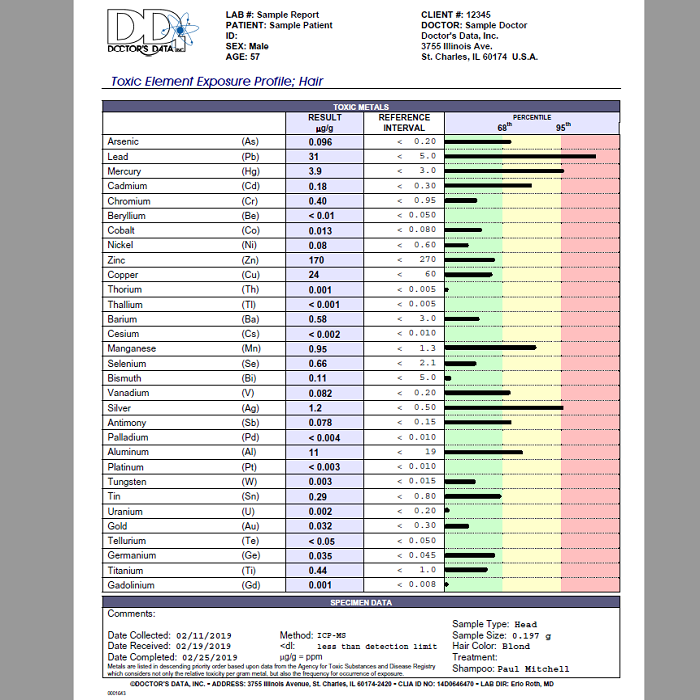
Doctors Data Hair Toxic Elements Test
$159.00$123.00Doctors Data Hair Toxic Elements Test is a noninvasive screening hair test reports an expanded lineup of toxic metals as well as specific nutrient elements.- Buy 2 at $119.00
Doctors Data Hair Toxic Elements Test
Health Tests, Toxic Metals Tests, Hair Tests, Autism Testing, Detox Solutions, Diabetes Solutions, Fatigue Solutions, Memory Loss Solutions$159.00 $123.00Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→

Trace Elements Nutritional Deficiencies Hair Test
$188.00 $148.00Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→

Analytical Research Labs Hair Test
$179.00$149.00Price during Father's Week Only
Providing a mineral blueprint of one’s biochemistry, an Analytical Research Labs Hair Minerals Test reports levels of minerals and heavy metals in your body giving possible reasons for your symptoms, with suggestions for nutritional supplements and diet changes. Hair tissue mineral analysis can provide pertinent information about balanced nutrition, one’s metabolic rate, energy levels, sugar and carbohydrate tolerance, stage of stress, immune system and glandular activity.- Buy 2 at $145.00
Analytical Research Labs Hair Test
$179.00 $149.00Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
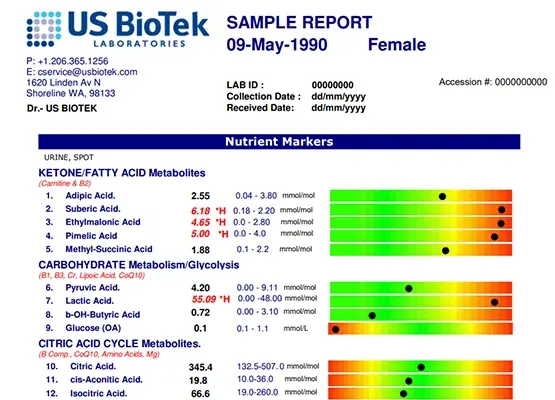
US BioTek Organic Acids Profile Environmental Pollutants Profile
$189.00A unique biochemistry profile called Organic Acid Test (OAT) can detect alterations in your gut, cellular deficiencies, levels of neurotrasmitters, exposures to mold or fungus and indicate need for specific nutrients, diet modifications and detoxification. Combine the OAT with the Environmental Pollutants Profile (EPP) for a more complete snapshot picture of toxic exposure to environmental chemicals.- Buy 2 at $185.00
US BioTek Organic Acids Profile Environmental Pollutants Profile
Health Tests, Nutritional Tests, Mycotoxin MoldsTests, Autism Testing, Environmental Pollutants Test, Organic Acids Test$189.00Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart...
Supplements
-
←→
Calcium Orotate
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Bone Solutions, Nerve Damage Solutions, Skin Solutions, Heart Solutions$26.80Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
Potassium Arginate with Aspartate
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Nerve Damage Solutions, Digestive Solutions, Muscle Solutions, Hormone Solutions, Heart Solutions$11.40Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
Magnesium Orotate
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Heart Solutions, Digestive Solutions, Immune System Solutions, Immune System Supplements$25.10Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
L-Lysine Orotate
$26.20L-Lysine Orotate 50 veggie capsulesMaximum quantity exceededMinimum purchase amount of 0 is requiredL-Lysine Orotate
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Candida Solutions, Skin Solutions, Bone Solutions, Immune System Solutions, Muscle Solutions, Heart Solutions$26.20Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
References
- https://store.mayoclinic.com/daily-living/bath-safety.html
- https://links.e.response.mayoclinic.org/EmailPreview-GeneralHealth
- https://my.rheumatology.org/rheumatology-provider-directory

