Table of Contents
Understanding Heart Health and Disease:
A Comprehensive Guide
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) encompasses a range of heart and blood vessel disorders, including heart attacks, strokes, and heart failure. It represents one of the leading causes of death worldwide, making it essential for health health enthusiasts to understand its causes, symptoms, and management. This guide aims to provide an empathetic yet persuasive overview of how individuals can take control of their heart health through lifestyle modifications, dietary choices, and appropriate medical interventions.
Causes of Cardiovascular Disease
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in determining an individual’s risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Family history of heart-related issues can predispose an individual to similar problems due to inheritance patterns of genes. For instance, genetic markers associated with high cholesterol levels or hypertension can be passed down through generations, influencing overall heart health. While one cannot change their genetic makeup, understanding familial patterns can help in early intervention and lifestyle adjustments.
Lifestyle Choices
Poor lifestyle choices are among the most significant contributors to cardiovascular disease. Sedentary behavior, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking can increase the risk of developing heart conditions. Regular physical activity, in contrast, promotes cardiovascular fitness and reduces weight, thereby lowering blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Embracing a balanced lifestyle can drastically improve heart health and mitigate risks.
Dietary Influences
The food we consume has a direct impact on our heart health. Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, where arteries narrow due to plaque buildup. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids can foster heart health. The Mediterranean diet, for example, has been associated with reduced heart disease rates due to its emphasis on healthy fats, lean proteins, and plant-based foods.
Environmental Factors
Environmental influences such as pollution and exposure to toxic substances can also contribute to cardiovascular disease. Studies show that long-term exposure to air pollution is linked to an increased incidence of heart attacks and strokes. Additionally, stressful living conditions, whether due to economic hardship or social strife, can exacerbate cardiovascular risk factors, highlighting the necessity for clean environments and supportive communities.
Symptoms of Cardiovascular Disease
Common Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of heart disease is vital for timely intervention. Common symptoms may include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, and palpitations. These symptoms can vary in intensity and frequency among individuals, making awareness critical for early diagnosis and treatment.
Warning Signs to Watch For Heart Disease
Warning signs that indicate a potential heart crisis include intense chest pain, radiating discomfort to the arms, neck, back, or jaw, sudden dizziness, or cold sweats. These symptoms, particularly when they appear unexpectedly, should be treated as emergencies. Understanding these signs can empower individuals to seek medical assistance promptly and save lives.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is essential to know when to seek medical help. If someone experiences persistent chest pain, difficulty breathing, or symptoms that worsen over time, contacting a healthcare professional immediately is crucial. Early evaluation can lead to timely treatment and potentially prevent severe complications.
Complications of Cardiovascular Disease
Heart Attack
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, usually by a blood clot. This blockage can cause substantial heart damage and can be fatal. Recognizing the signs of a heart attack can be life-saving, and immediate medical intervention is necessary.
Stroke
Stroke results from interrupted blood flow to the brain, which can lead to brain damage and disability. There are two types of strokes: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Quick recognition of stroke symptoms, often summarized with the acronym FAST (Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulties, Time to call emergency services), can lead to better outcomes.
Heart Failure
Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently, leading to fluid buildup and other complications. Symptoms may include fatigue, swelling in the legs, and difficulty breathing. Management often requires a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and possibly surgery.
Peripheral Artery Disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) involves narrowed arteries reducing blood flow to limbs, often causing leg pain and mobility issues. Recognizing PAD early is essential, as it can lead to severe complications, including infections and the need for surgical intervention.
Management of Cardiovascular Disease
Lifestyle Modifications
Managing cardiovascular disease effectively often starts with significant lifestyle modifications. Incorporating regular physical activity, reducing alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking are critical steps. Establishing a consistent exercise routine—aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity weekly—can enhance cardiovascular health and improve overall fitness levels.
Medical Treatments
In conjunction with lifestyle changes, medical treatments play an essential role in managing cardiovascular disease. Patients may require medications to control high blood pressure, cholesterol levels, or blood sugar. In some cases, surgical interventions like angioplasty or bypass surgery may be necessary to restore proper blood flow.
Importance of Regular Check-Ups
Routine check-ups with healthcare providers allow for monitoring heart health and assessing risk factors. Regular screenings for blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and diabetes can aid in early detection and intervention. Maintaining open lines of communication with healthcare professionals is vital for effective management and prevention of cardiovascular complications.
The Role of Magnesium in Heart Health
Magnesium’s Function in Cellular Processes
Magnesium is a crucial mineral that plays a significant role in various cellular processes, including energy production and muscle function. It is vital for maintaining normal blood pressure and supporting the contraction and relaxation of heart muscles. Adequate magnesium levels promote cardiovascular health, helping to prevent hypertension and arrhythmia’s.
Energy Production and Muscle Relaxation
As a co-factor in many enzymatic reactions, magnesium is essential for ATP production, the energy currency of cells. This energy is vital for heart muscle contraction. Additionally, magnesium helps to relax blood vessels, enhancing circulation and reducing the workload on the heart. A deficiency in magnesium can lead to muscle cramps, spasms, and increased heart disease risk.
Consequences of Low Magnesium Levels
Low magnesium levels can correlate with increased cardiovascular disease risk. Studies have shown that magnesium deficiency may contribute to high blood pressure, arterial stiffness, and inflammation. Addressing magnesium deficiency may help lower the risk of developing heart-related issues.
Factors Contributing to Magnesium Depletion
Several factors can lead to magnesium depletion, including poor dietary choices, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions. Additionally, stress and physical inactivity can exacerbate magnesium loss in the body. Combating these factors through dietary modification and lifestyle changes is essential for maintaining adequate magnesium levels.
Essential Minerals and Their Impact
The Role of Calcium in Heart Health
Calcium is well-known for its role in bone health, but it is also crucial for the heart. Calcium aids in the contraction and relaxation of heart muscles. However, an excess of calcium, particularly when combined with low magnesium intake, can lead to arterial stiffness and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Thus, maintaining a proper balance of these minerals is essential for heart health.
The Importance of Sodium and Potassium Balance
Sodium and potassium work in tandem to regulate blood pressure and maintain proper fluid balance in the body. High sodium intake is often linked with hypertension, while adequate potassium can counteract the negative effects of sodium. Incorporating potassium-rich foods, such as bananas, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens, is beneficial for cardiovascular health.
Copper: A Vital Trace Element
Copper is a trace mineral that plays a role in iron metabolism and the maintenance of blood vessels. It contributes to the formation of collagen, which is essential for blood vessel integrity. Insufficient levels of copper can lead to cardiovascular complications, highlighting the importance of a well-rounded diet rich in diverse minerals.
Zinc’s Role in Cardiovascular Function
Zinc is another essential mineral that contributes to cardiovascular health. It plays a role in maintaining healthy endothelial function, which is crucial for proper blood flow. Zinc deficiency has been linked to increased inflammatory markers and cardiovascular risk. Ensuring adequate zinc intake through diet or supplementation may support heart health.
Toxic Metals and Their Effects on Heart Health
High Iron Levels
While iron is necessary for producing hemoglobin and transporting oxygen in the blood, excessive iron accumulation can lead to oxidative stress and damage to blood vessels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. It is vital to monitor iron levels, particularly in individuals with hereditary hemochromatosis or those receiving frequent blood transfusions.
The Impact of Lead and Cadmium
Lead and cadmium are toxic metals known to adversely affect cardiovascular health. Exposure to these metals can lead to hypertension and atherosclerosis. Reducing exposure to environmental pollutants and advocating for cleaner air and water are essential for protecting cardiovascular health from these harmful substances.
Cadmium’s Role in Arterial Brittle
Cadmium exposure may contribute to arterial stiffness, a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. This heavy metal can impair endothelial function and promote inflammation in blood vessels. Minimizing exposure through dietary choices and environmental awareness is crucial for maintaining heart health.
The Influence of Emotions and Lifestyle on Heart Health
Stress Management Techniques
Emotional well-being plays a critical role in cardiovascular health. Chronic stress can lead to increased blood pressure and heart rate, heightening the risk of heart disease. Learning stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and regular physical activity can mitigate these risks. Prioritizing mental health is not only beneficial for emotional stability but also essential for maintaining a healthy heart.
The Connection Between Mental Health and Cardiovascular Disease
There is a growing body of evidence linking mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression, with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Mental health can influence lifestyle choices, adherence to treatment, and overall health outcomes. Engaging in comprehensive care that addresses both physical and mental health is paramount for promoting cardiovascular health.
Supplementation for Heart Health
The Benefits of Vitamin C and Vitamin E
Vitamins C and E are antioxidants that play a role in protecting the cardiovascular system from oxidative stress. Vitamin C can enhance endothelial function, while Vitamin E may help prevent the oxidation of LDL cholesterol. Including these vitamins in one’s diet through fruits, vegetables, and nuts can support heart health.
Chromium and Its Role
Chromium is essential for glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, which are crucial for reducing the risk of diabetes-related cardiovascular complications. Maintaining optimal chromium levels through diet or supplementation may support heart health and enhance metabolic function, making it a valuable addition to heart-healthy strategies.
Selenium and Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Selenium is another trace mineral that helps protect the heart from oxidative damage and inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and ability to lower triglyceride levels. Including foods rich in these nutrients can significantly enhance cardiovascular health and reduce disease risk.
Role of Other Nutritional Supplements
The significance of saturated fat consumption in relation to heart disease cannot be underestimated. It holds particularly crucial significance for individuals who are slow oxidizers and face challenges in processing fats. Dr. Dean Ornish has successfully showcased the potential for reversing the formation of arterial plaques through a powerful combination of adopting a low-fat, vegetarian diet, engaging in meditation, and incorporating regular exercise. Let’s embrace this transformative approach to enhance our heart health and overall well-being.
Dr. Robert Atkins, a cardiologist based in New York, made a significant discovery regarding heart disease treatment. He found that incorporating a low-carbohydrate diet alongside appropriate fat consumption can be immensely beneficial, particularly for individuals who are likely fast oxidizers. By introducing specific fats and oils into their diet, these individuals can restore balance to their body chemistry and experience notable improvements in their overall health.
Conclusion: Taking Charge of Your Symptoms of Heart Health
Understanding the symptoms of heart health entails recognizing its causes, symptoms, and management strategies. By making informed lifestyle decisions, addressing dietary needs, and fostering emotional well-being, individuals can take proactive steps toward heart health. Recognizing the vital role minerals play, alongside avoiding toxic substances, can further enhance cardiovascular outcomes.
FAQ’s
What are the early signs of cardiovascular disease?
Early signs may include chest discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, or palpitations. It’s crucial to recognize these symptoms and consult a healthcare provider.
How does diet affect heart health?
A heart-healthy diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats while limiting saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol. This balance can reduce the risk of heart disease.
Can stress impact heart health?
Yes, chronic stress can lead to increased blood pressure and heart rate, contributing to a higher risk of heart disease. Managing stress through techniques like mindfulness is beneficial.
What role do supplements play in heart health?
Supplements like vitamins C and E, omega-3 fatty acids, Magnesium and trace minerals can support heart health by providing essential nutrients that combat oxidative stress and reduce inflammation.
How often should I get my heart checked?
Regular check-ups are vital for monitoring heart health. Individuals should aim for annual check-ups, but those with risk factors may need more frequent evaluations.
At Home Tests
-
←→
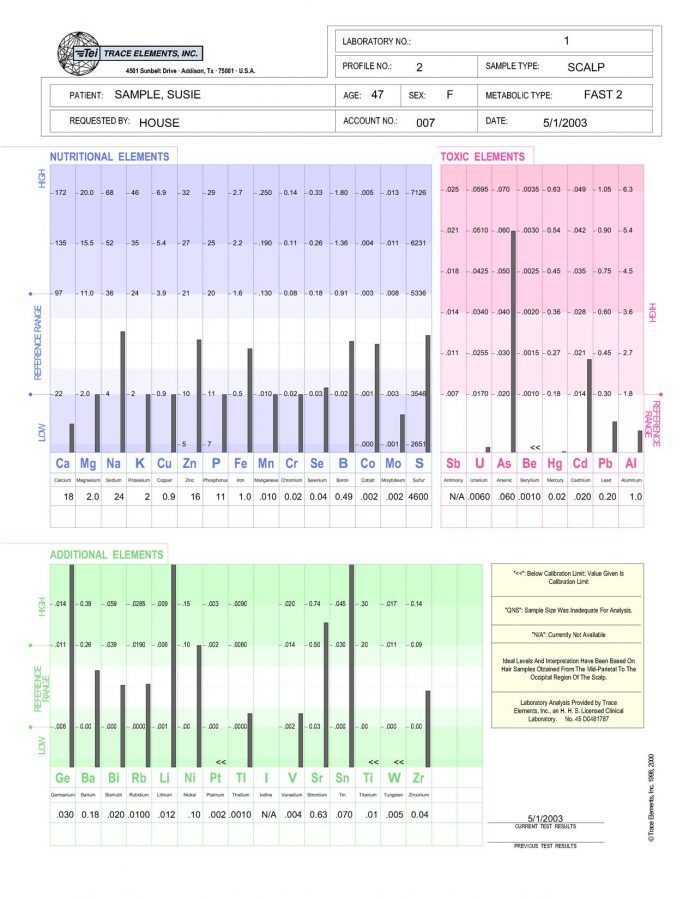
Trace Elements Nutritional Deficiencies Hair Test
Nutritional Tests, At Home Health Tests, Toxic Metals Tests, Hair Tests, Autism Tests, Vitamin Supplements$188.00 $148.00Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→

Analytical Research Labs Hair Test
$179.00$149.00Providing a mineral blueprint of one’s biochemistry, an Analytical Research Labs Hair Minerals Test reports levels of minerals and heavy metals in your body giving possible reasons for your symptoms, with suggestions for nutritional supplements and diet changes. Hair tissue mineral analysis can provide pertinent information about balanced nutrition, one’s metabolic rate, energy levels, sugar and carbohydrate tolerance, stage of stress, immune system and glandular activity.- Buy 2 at $145.00
Analytical Research Labs Hair Test
$179.00 $149.00Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart...
Products
-
←→
Magnesium Orotate
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Heart Solutions, Digestive Solutions, Immune System Solutions, Immune System Tests$25.10Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→

Potassium Orotate
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Skin Solutions, Diabetes Solutions, Heart Solutions, Muscle Solutions, Digestive Solutions, Hormone Solutions$23.40Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
K-MG Potassium Magnesium
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Headache Solutions, Heart Solutions, Muscle Solutions, Lung Solutions, Memory Loss Solutions, Anxiety, Stress, Depression Solutions$13.10Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→

GTF Chromium Glucose Tolerance Factor
$4.60GTF Chromium Glucose Tolerance Factor with 200 mcg ChromiumGTF Chromium Glucose Tolerance Factor
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Adrenal Fatigue Solutions, Diabetes Solutions, Skin Solutions, Heart Solutions, Muscle Solutions, Anxiety, Stress, Depression Solutions$4.60Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
-
←→
-
←→
Lithium Orotate
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Autism Solutions, Digestive Solutions, Nerve Damage Solutions, Immune System Tests, Immune System Solutions$16.30Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
Carotavit with Selenium Charge Sustained
$23.40Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
Selenium
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Immune System Tests, Heart Solutions, Immune System Solutions, Hormone Solutions$13.10Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart...
References
- https://links.e.response.mayoclinic.org/EmailPreview-GeneralHealth
- https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/headache
- http://millionhearts.hhs.gov/
- http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/
- https://wonder.cdc.gov/mcd.html
- https://www.testing.com/tests/high-sensitivity-c-reactive-protein-hs-crp/
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/resources/take-action-your-heart-get-started-fact-sheet
- https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/tips/things-to-know-about-omegas-for-heart-disease
- https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack/treatment-of-a-heart-attack/cardiac-medications
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/heart-healthy-living
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/heart
- https://www.heart.org/en/

