
Table of Contents
Introduction to Gut Brain Connection
The gut-brain connection is a fascinating area of study that explores how our digestive system influences mental well-being and cognitive function. As research advances, it becomes increasingly evident that gut health is not merely about digestion but is intricately linked to emotional and psychological states. In this article, we will delve into the scientific principles underpinning the gut-brain axis, how gut health impacts mental well-being, and actionable strategies for improving gut health to enhance cognitive function.
The Importance of Gut Health
The gut is often referred to as the second brain due to its complex network of neurons and its crucial role in our overall health. With over 100 trillion microorganisms residing in the gut, this microbiome significantly influences various bodily functions, including digestion, immune response, and even mood regulation. An imbalance in gut microbiota can lead to a series of health issues, ranging from gastrointestinal disorders to mental health conditions.
Defining the Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain connection refers to the bidirectional communication between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain. This process involves multiple pathways, including nerve signals, hormones, and immune system responses. The gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in this connection, affecting neurotransmitter production and modulating stress responses.
The Science Behind the Gut-Brain Axis
Neurotransmitters and Gut Microbiota
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals in the brain. An astonishing 90% of serotonin, often called the feel-good neurotransmitter, is produced in the gut. This production is heavily influenced by gut microbiota. Studies suggest that specific strains of probiotics can increase serotonin levels, thereby improving mood and emotional well-being. The interplay between gut health and neurotransmitter production underscores the critical relationship between what we eat and how we feel.
If you are looking for a good probiotic that has
The Role of the Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve serves as a primary communication pathway between the gut and the brain. It transmits signals regarding gut health and digestion directly to the brain, influencing mood and cognitive function. Stimulation of the vagus nerve has been shown to alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression, demonstrating the importance of this nerve in the gut-brain connection.
Impact of Inflammation on Mental Health
Chronic inflammation in the gut can significantly affect mental health. Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are often associated with increased levels of inflammatory markers, which can lead to mood disorders such as anxiety and depression. The gut microbiome’s balance is essential for maintaining a healthy inflammatory response, making it a key target for therapeutic interventions.
How Gut Health Influences Mental Well-Being
The Link Between Gut Microbiota and Mood Disorders
Recent research has established a clear connection between gut microbiota composition and mood disorders. A diverse and balanced microbiome is linked to lower levels of anxiety and depression. Conversely, an imbalance in gut bacteria, known as dysbiosis, can contribute to increased anxiety, depression, and even cognitive decline. Understanding this relationship paves the way for innovative treatments that aim to restore gut health for better mental well-being.
Gut Health and Stress Response
The gut also plays a crucial role in how we respond to stress. During stressful situations, the gut may react by altering its microbiota composition, which can exacerbate feelings of anxiety or depression. Furthermore, stress can affect gut permeability, leading to a phenomenon known as leaky gut, where toxins and bacteria can enter the bloodstream, triggering inflammatory responses that affect the brain. Addressing gut health can significantly improve your resilience to stress. A test to help you know the state of your microbiota composition is from Doctor’s Data.
Probiotics and Their Effects on Anxiety and Depression
Probiotics, often referred to as good bacteria, have gained popularity for their potential mental health benefits. Research indicates that specific probiotic strains may help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression. By restoring balance to gut microbiota, probiotics not only improve digestive health but also positively influence mood and emotional well-being. Incorporating fermented foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, can be a delicious and effective strategy to support mental health.
Improving Your Gut Health for Better Cognitive Function
Dietary Changes to Support Gut Health
Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy gut. A diet rich in fiber, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries and leafy greens, can also reduce inflammation in the gut, promoting overall health. On the other hand, a diet high in processed foods and sugars can lead to dysbiosis, negatively impacting both gut and mental health. Making conscious dietary choices is essential for fostering a healthier gut-brain connection.
Incorporating Prebiotics into Your Diet
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial bacteria in the gut. Foods rich in prebiotics include garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus. By incorporating these foods into your diet, you can enhance the growth and activity of good bacteria, promoting a balanced gut microbiome. This, in turn, can improve mood and cognitive function, showcasing the powerful link between diet and mental health.
Choosing the Right Probiotic Supplement
While dietary sources of probiotics are beneficial, supplements can also be an effective way to enhance gut health. However, not all probiotics are created equal. When selecting a probiotic supplement, it’s essential to choose those with clinically researched strains that have been shown to support mental health and cognitive function. By the time you buy a probiotic off the shelf, there’s no way to know if the bacteria in it are as active as they were as when the product was made.” Johns Hopkins Medicine Can Probiotics Improve Your Mood?
Here at Health Always Dr. Psonak recommends Innate Response Formula 20-14 that has 14 beneficial strains and 20 billion cultures of active bacteria.
The Future of Gut Health Research
Emerging Studies on Gut Microbiota and Cognitive Decline
As research into the gut-brain connection evolves, new studies continue to reveal the potential of gut microbiota in preventing cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases. Emerging evidence suggests that targeting the gut microbiome may play a role in conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Innovative therapeutic approaches that focus on gut health may pave the way for groundbreaking treatments in the future.
Potential Therapeutic Approaches
Future interventions may not only focus on probiotics and dietary changes but also explore the use of prebiotics, dietary fibers, and even fecal microbiota transplants (FMT) as potential treatments for mental health disorders. These approaches could significantly alter the landscape of mental health treatment, emphasizing the need for holistic strategies that consider gut health as a vital component of overall well-being.
Conclusion
The gut-brain connection is a testament to the complex interplay between our digestive health and mental well-being. As we continue to unravel the intricacies of this relationship, it becomes clear that improving gut health can have profound effects on mood, stress responses, and cognitive function. By making informed dietary choices, incorporating probiotics and prebiotics, and staying attuned to ongoing research, we can harness the power of the gut-brain connection to enhance our mental health and overall quality of life.
FAQ’s
What are probiotics, and how do they benefit gut health?
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer health benefits. They help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, improve digestion, and may positively impact mental health by influencing neurotransmitter production.
Can a poor diet affect my mental health?
Yes, a diet high in processed foods and sugars can contribute to an imbalanced gut microbiome, leading to increased inflammation and a higher risk of mood disorders.
How long does it take to see improvements in gut health after dietary changes?
While some individuals may notice improvements in a few weeks, significant changes in gut health can take several months of consistent dietary adjustments.
Are there any risks associated with taking probiotics?
In general, probiotics are considered safe for most individuals. However, those with compromised immune systems should consult a healthcare provider before starting any probiotic regimen.
What are prebiotics, and how do they differ from probiotics?
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial bacteria in the intestine, while probiotics are live bacteria that provide health benefits. Both are essential for maintaining gut health.
Products for a Healthy Gut Brain Connection
At Home Tests for Gut Brain Health
-
←→

Doctors Data Microbiology Stool Test
$149.00The Doctors Data Microbiology Stool Test identifies bacteria in the stool, yeast in the stool, the presence of imbalanced flora, and beneficial flora. This test identifies Clostridium species, and dysbiotic flora, as well as infectious pathogens.- Buy 2 at $164.00
Doctors Data Microbiology Stool Test
At Home Health Tests, Gastrointestinal Tests, Probiotics, Irritable Bowel Solutions, Inflammation Solutions, Immune System Solutions, Digestive Solutions, Gastrointestinal Issues$149.00Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→

Doctors Data Comprehensive Stool Analysis
$549.00$358.00Doctors Data Comprehensive Digestive Stool Analysis helps pinpoint the causes of gastrointestinal issues, symptoms and chronic systemic conditions, by measuring key markers of digestion, absorption and inflammation.- Buy 2 at $350.00
Doctors Data Comprehensive Stool Analysis
At Home Health Tests, Gastrointestinal Tests, Probiotics, Inflammation Solutions, Digestive Solutions, Skin Solutions, Irritable Bowel Solutions, Gastrointestinal Issues$549.00 $358.00Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
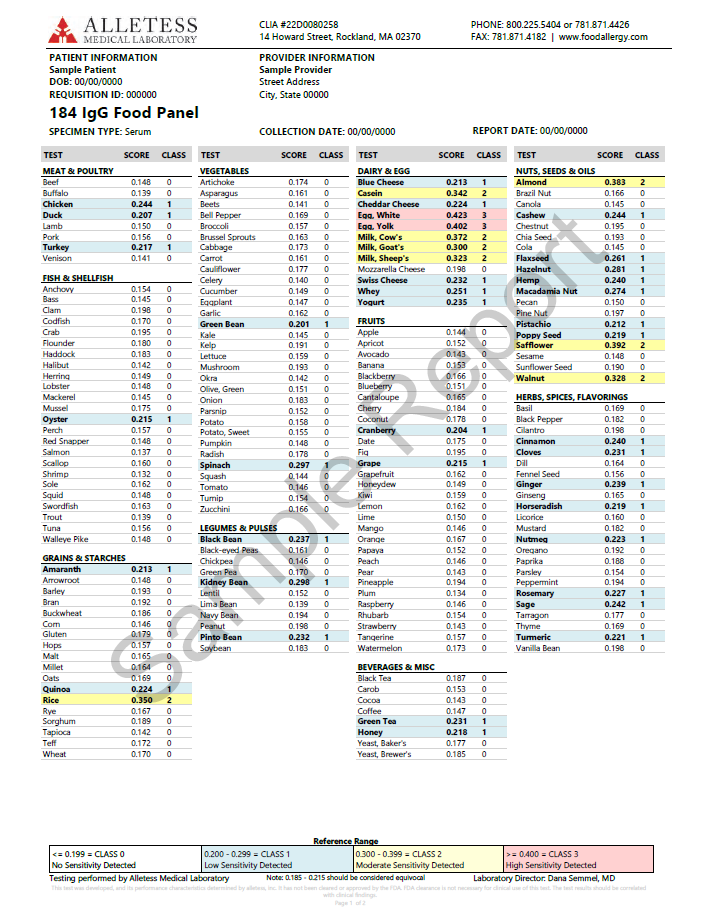
Alletess Food Allergy Sensitivity Test
$269.00$223.00Food sensitivities may be causing many of your health issues. Test now with this convenient at home test; no lab visit required.Alletess Food Allergy Sensitivity Test
At Home Health Tests, Allergy Tests, Blood Spot Tests, Allergy Solutions, Lung Solutions, Gastrointestinal Issues$269.00 $223.00Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→

UCARI Intolerance Test Kit
$99.99$88.00Test for 1500+ possible intolerances and nutritional imbalances- Buy 2 at $85.00
UCARI Intolerance Test Kit
At Home Health Tests, Hair Tests, Allergy Tests, Nutritional Tests, Environmental Pollutants Tests, Mycotoxin Molds Tests, Allergy Solutions, Lung Solutions, Gastrointestinal Issues$99.99 $88.00Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart...
Supplements
-
←→
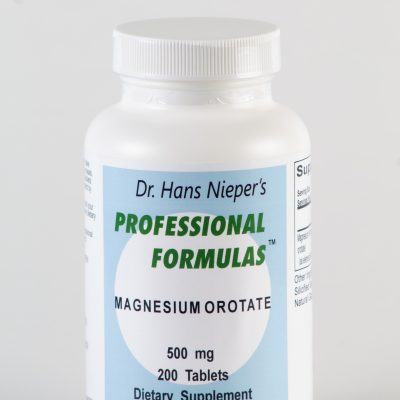
Magnesium Orotate
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Heart Solutions, Digestive Solutions, Immune System Solutions, Immune System Tests$25.10Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→

Membrane Complex
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Heart Solutions, Immune System Tests, Skin Solutions, Digestive Aids, Bone Solutions, Lung Solutions, Muscle Solutions$15.00Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
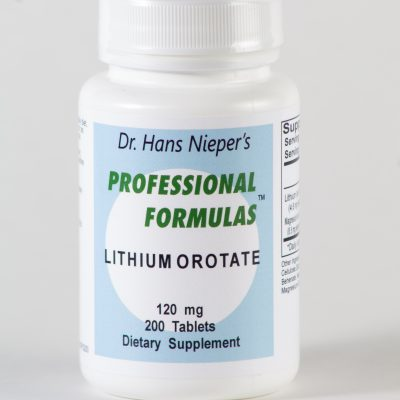
Lithium Orotate
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Autism Solutions, Digestive Solutions, Nerve Damage Solutions, Immune System Tests, Immune System Solutions$16.30Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→

-
←→
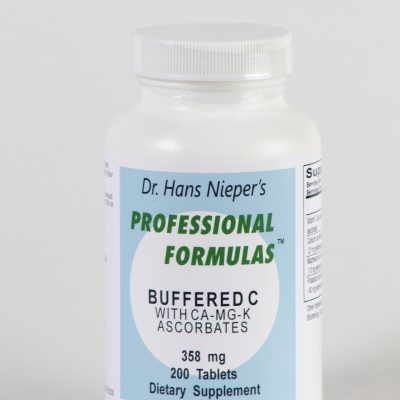
Buffered C with Calcium, Magnesium & Potassium
Supplements, Vitamin Supplements, Immune System Tests, Skin Solutions, Constipation Solutions, Cancer Solutions$11.70Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→
Selenium
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Immune System Tests, Heart Solutions, Immune System Solutions, Hormone Solutions$13.10Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart... -
←→

GTF Chromium Glucose Tolerance Factor
$4.60GTF Chromium Glucose Tolerance Factor with 200 mcg ChromiumGTF Chromium Glucose Tolerance Factor
Supplements, Mineral Supplements, Adrenal Fatigue Solutions, Diabetes Solutions, Skin Solutions, Heart Solutions, Muscle Solutions, Anxiety, Stress, Depression Solutions$4.60Successfully Added to your Shopping CartAdding to Cart...


Hello,
I came across your profile on social media and noticed you have an impressive base of followers and some great reviews. It looks like you have built a strong community.
Regards,
Josette
Dear Sir/Madam, I am very much interedted please send me more details